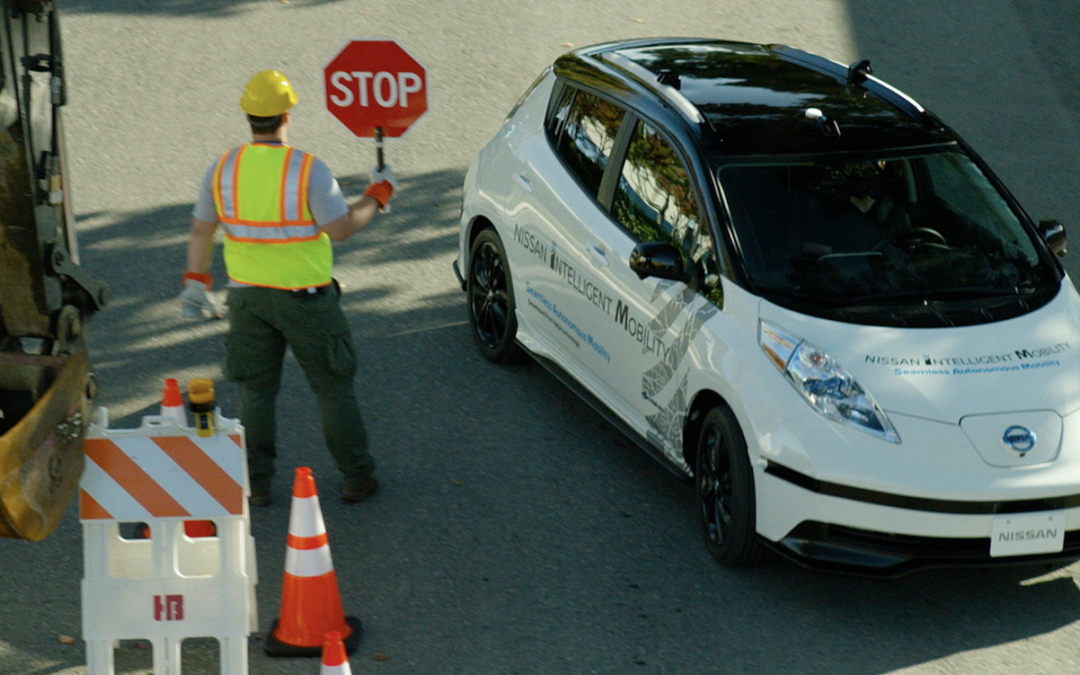
Case Study—This case study presents ethnographic work in the midst of two fields of technological innovation: automated vehicles (AV) and virtual reality (VR). It showcases the work of three MSc. Techno-Anthropology students and their collaboration with the EU H2020 project ‘interACT’, sharing the...