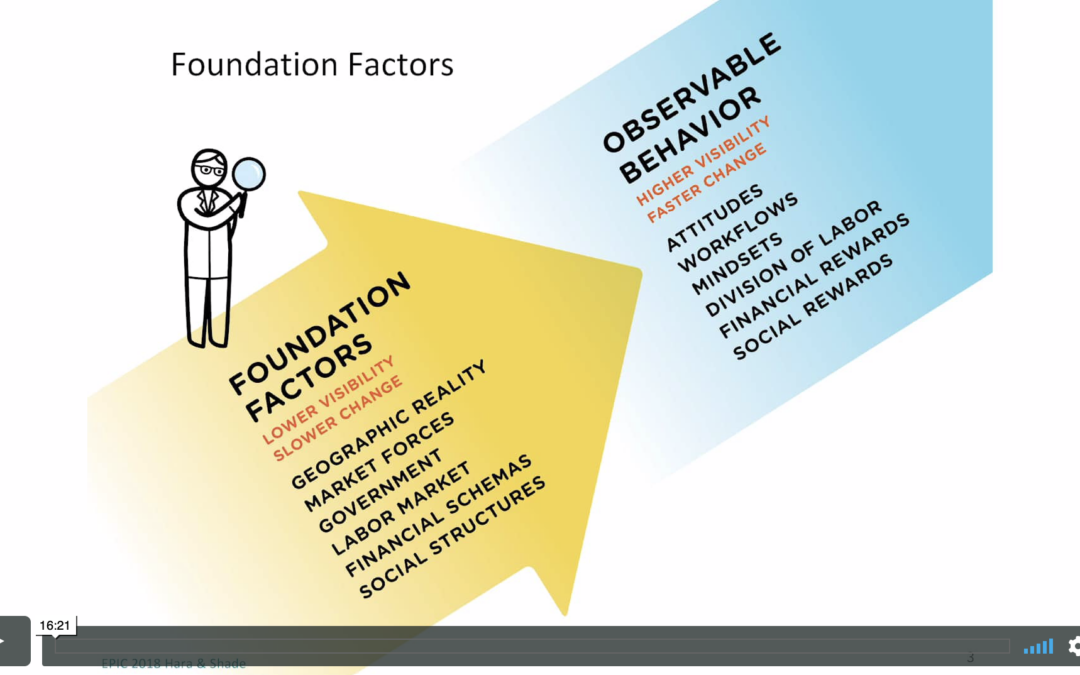
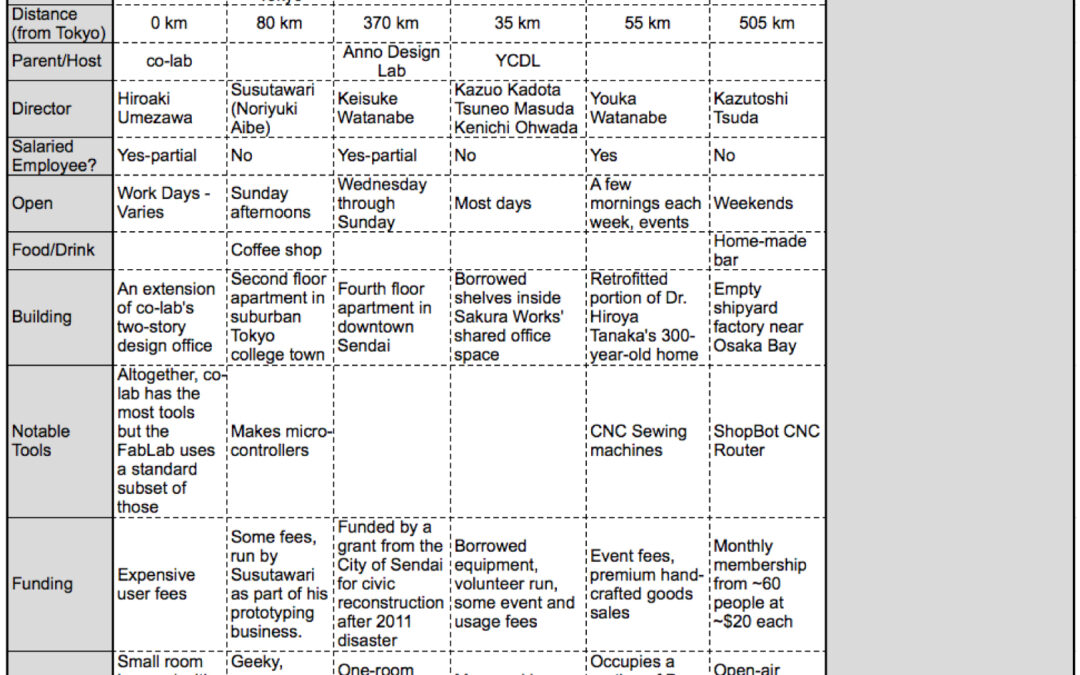
In international business ethnography, clients and subjects don’t share the same background. Without an understanding of the underlying factors affecting the subject’s behaviors, data can lead to false home-market based assumptions about cause and effect. Where do we as researchers look to detect...