This paper presents ethnographic studies of hard of hearing (HoH) users that had significant impacts on the...


This paper presents ethnographic studies of hard of hearing (HoH) users that had significant impacts on the...

John W. Sherry, Director the Experience Innovation Lab at Intel Corporation, is a Keynote Speaker at EPIC2016—join us! “Anthropology is really undersold.” Dr. John Sherry’s words carry weight—he is Director of the Experience Innovation Lab at Intel Corporation. In addition to discovering ways to...

This case demonstrates how ongoing ethnographic research from within a corporation led to the re-segmentation of a market. The first part of the case focuses on how a team of social science researchers at a major technology company, Intel, drew on past research studies to develop a point-of-view...

This is a piece about certain types of objects. Those objects are models. I want to suggest that models are objects that are central to the various practices in which EPIC People are engaged for three reasons. Firstly, they help manage situations of uncertainty. Second, they are tools for...
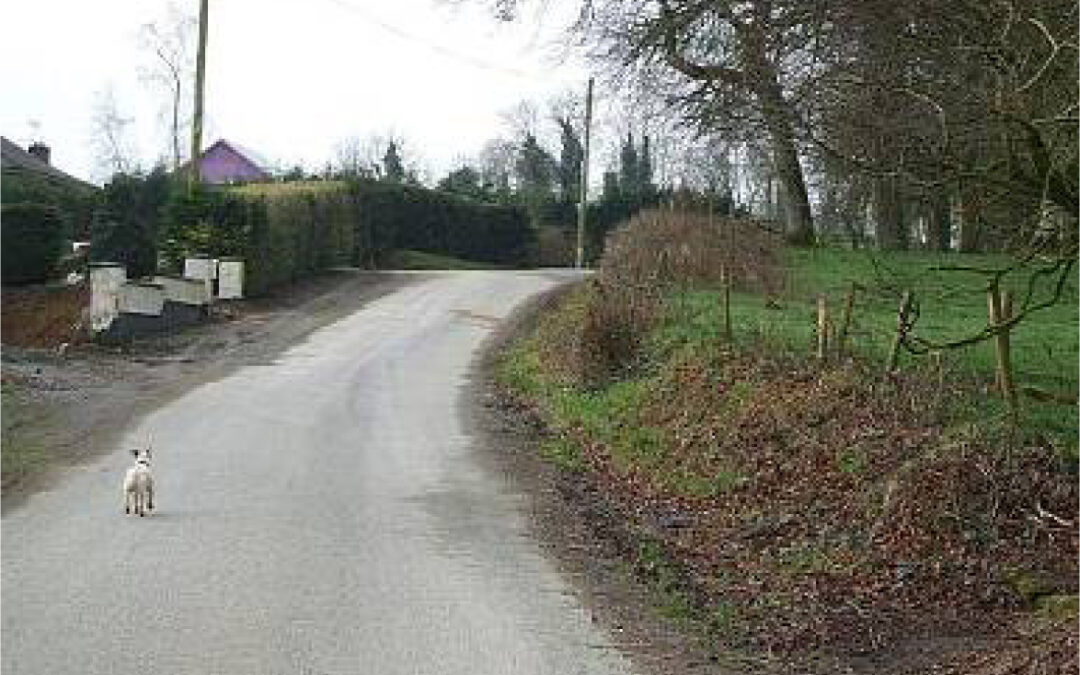

This paper, based on a fieldwork conducted with community transport projects in rural Ireland, examines the place of mobility in the lives of older people. It uses the idea of journey to explore what mobility means to older people, what the research made visible to a diverse range of project...

Staying relevant (to the business) is at the heart of career-advancement and (increasingly) job-security, particularly, in a business unit. It embodies a number of different meanings to the different players in corporate—from supporting product definition to creating strategic plans to making the...
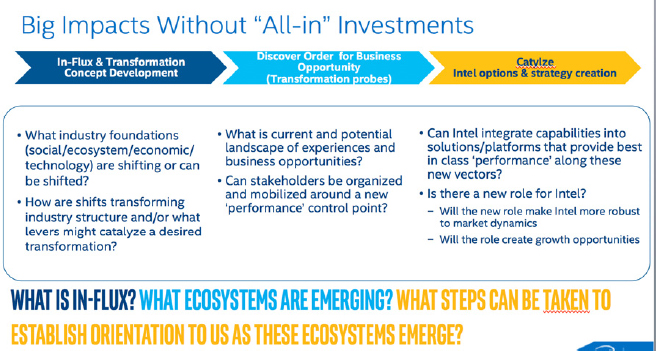
While ethnography has been integrated into the design research, new product development and corporate strategy, it has been less well integrated into path-finding for new business opportunities. We’ve developed a model for path-finding research that has three core parts: creating a business...

EPIC Profiles Series A PhD in French Literature and Cultural Studies from Duke University (1988-1994), Maria Bezaitis may appear to have a surprising career as a scientist inside Intel’s Interaction and Experience Lab. But as she says, her vast literary studies exploring modernist literary...

This paper examines the politics of visibility – the ways in which the work of ethnographers is positioned inside and outside organizations not only as means of unpacking the “real-world” but often as means to create business and marketing differentiation. We contend that the institutional...

Researchers at EPIC face something of a trap. Situated in an ethos of twenty first century consumer capitalism, our professional duties overemphasize individual consumers, and the products of our research always diverge towards our respective corporations’ interests. As a result we have little...